Claims insights: neurosurgeons
What are the main issues driving neurosurgeon members' compensation claims and complaints? Find out the underlying themes and insights to reduce your risk of these types of claims and complaints.
Wednesday, 16 April 2025
| Overview | Practice points |
|
|
Incidence and breakdown by type of matter are based on all matters indemnified by Avant for neurosurgeons from FY 2020-24. Underlying themes and assessment of care are based on Avant claims and complaints closed from FY 2020-24.
1 in 4*
Avant neurosurgeon members per year were subject to one or more matters relating to their provision of health care (*five-year average).
The types of medico-legal matters included claims for compensation (48%), regulatory complaints (40%), coronial (6%), employment disputes (4%) and other matters (3%).
Main issue in claims and complaints

Stage of care where surgical issues occurred
- Pre-operative (26%) e.g. allegations of improper selection of procedure/surgery/surgical approach
- Intra-operative (64%) e.g. allegations of poor surgical performance/skill/competence as a result of complications such as pain or nerve damage; failure, misuse or improper insertion of medical device/prosthesis/fixation
- Post-operative (10%) e.g. delay/failure to diagnose complications.
(% of total procedural/surgical issues)
Most common procedures involved in procedural/surgical allegations
| Spinal surgeries (74%) | Cranial surgeries (15%) |
Most common were:
| Most common was:
|
(% of total procedural/surgical issues)
Consent and communication
While almost 70% of claims and complaints were about procedural/surgical issues, some of these contained more than one allegation.
- One in three cases had an additional allegation of poor consent (e.g. inadequate or no discussion of risks, consent not obtained for procedure, treatment or test)
- One in six cases had an additional allegation of poor communication (e.g. failure to communicate results/ information to patient, patient or family felt uninformed/condition not explained adequately).
(The above incidences were based on cases that had procedural/surgical issues as the primary allegation and consent or communication issues as secondary allegations.)
Assessment of the care provided
Experts and/or regulators assessed the care provided and found:
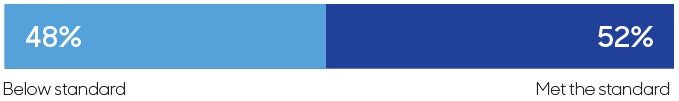
(% of complaints/claims where the assessment of the expected standards on the main factor is known.)
Glossary
- Matters include claims, complaints, coronial cases and other matters such as employment disputes and Medicare.
- Claims refers to claims for money, compensation and civil claims.
- Complaints relates to formal complaints to regulators including Ahpra, HCCC in NSW and OHO in Queensland.
- Employment disputes are matters where Avant defends members against complaints or supports members to resolve employment issues.
- Medicare matters include Medicare investigations and audits.
More information
For medico-legal advice, please contact us here, or call 1800 128 268, 24/7 in emergencies.
For any queries on this analysis, please contact us at research@avant.org.au.
MPORTANT: Avant routinely codes information collected in the course of assisting member doctors in medico-legal matters into a standardised, deidentified dataset. This retrospective analysis was conducted using this dataset. The findings represent the experience of these doctors in the period of time specified, which may not reflect the experience of all doctors in Australia. This publication is not comprehensive and does not constitute legal or medical advice. You should seek legal or other professional advice before relying on any content, and practise proper clinical decision-making with regard to the individual circumstances. Persons implementing any recommendations contained in this publication must exercise their own independent skill or judgement or seek appropriate professional advice relevant to their own particular practice. Compliance with any recommendations will not in any way guarantee discharge of the duty of care owed to patients and others coming into contact with the health professional or practice. Avant is not responsible to you or anyone else for any loss suffered in connection with the use of this information. Information is only current at the date initially published [April 2025].
More ways we can help you



